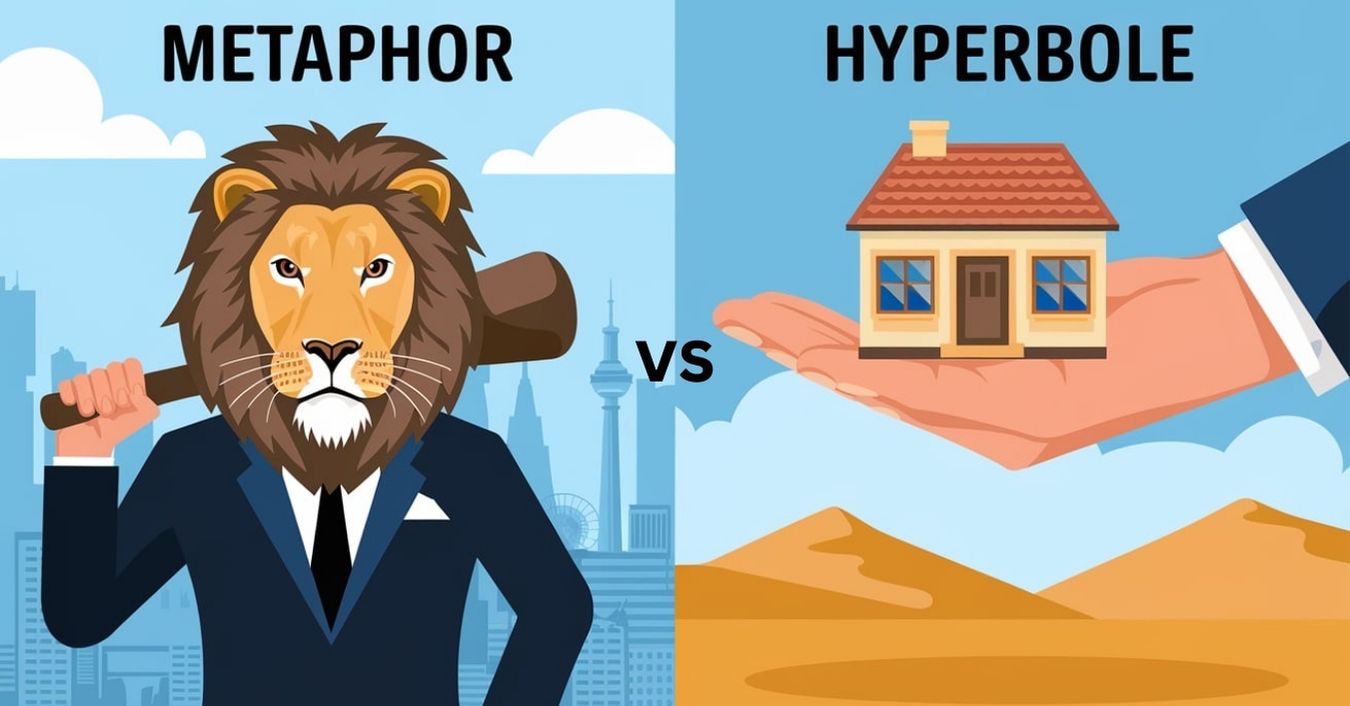
Metaphor vs Hyperbole are two powerful literary devices used to enhance language, but they serve different purposes. A metaphor creates a direct comparison between two unrelated things, making abstract concepts easier to understand.
On the other hand, hyperbole is an intentional exaggeration used for emphasis or humor. While both are forms of figurative language, they function differently in speech and writing.
Understanding the difference between metaphor and hyperbole helps improve communication and creative expression. Writers, poets, and advertisers use these techniques to make their messages more engaging.
This article explores their meanings, examples of metaphor and examples of hyperbole, and how they appear in metaphor vs hyperbole in literature and everyday speech.
Understanding metaphor vs hyperbole
A metaphor is a figure of speech that compares two unrelated things to create deeper meaning. It helps paint vivid images in the reader’s mind, like “Time is a thief.
A hyperbole, on the other hand, is an exaggerated statement not meant to be taken literally, such as “I’ve told you a million times.” Both are powerful literary devices, but while metaphors create symbolic meaning, hyperboles amplify emotions.
Writers use them to make their language more expressive, engaging, and impactful in storytelling and everyday speech.
Origins of the metaphor
The use of metaphors dates back to ancient civilizations, where people used symbolic language to explain complex ideas. Greek philosopher Aristotle first studied metaphors in depth, describing them as a tool to understand one thing through another.
Over time, metaphors became essential in literature, philosophy, and everyday speech. They help shape human thought, making abstract concepts easier to grasp.
Today, they play a key role in Natural Language Understanding (NLU) and computational linguistics, allowing AI to interpret and process figurative language more effectively.
Origins of the hyperbole
The concept of hyperbole has been present in language for centuries, dating back to ancient Greek and Roman rhetoric. Orators and poets used extreme exaggeration to emphasize emotions and persuade audiences.
Over time, hyperbole became a key tool in storytelling, humor, and persuasive writing. From mythology to modern advertising, it helps grab attention and create lasting impressions.
Today, hyperbole is widely used in literature, speech, and even sentiment analysis in metaphors, as AI and computational linguistics work to identify and process exaggerated expressions in digital text.
metaphor: Definition and Usage
A metaphor is a way of comparing two different things by saying one thing is another. It does not use “like” or “as” like a simile does. Instead, it creates a direct connection to make an idea more powerful.
For example, “Her smile is sunshine” means her smile brings warmth and happiness, just like the sun. Metaphors are commonly used in literature, poetry, and everyday speech to add depth and emotion. They help express thoughts creatively and make language more engaging and meaningful.
metaphor Usage
Metaphors are used in everyday speech, literature, poetry, and even advertising to make language more vivid and expressive. They help simplify complex ideas by relating them to familiar concepts.
In storytelling, metaphors create deeper meaning and emotion, making descriptions more engaging. For example, “The world is a stage” suggests that life is like a play where people act out different roles.
In business and marketing, metaphors make messages more persuasive, such as “building a brand” to describe growing a company. Their power lies in making abstract ideas easier to understand and more memorable.
Synonyms of metaphor
While “metaphor” is the most precise term, here are some related concepts:
- Analogy
- Symbol
- Figure of speech
- Image
- Trope
- Allegory
- Representation
- Comparison
- Parable
- Simile (though similes use “like” or “as”)
Hyperbole vs Metaphor: Key Differences
Hyperbole vs metaphor are both figures of speech, but they serve different purposes. A metaphor makes a direct comparison between two things by saying one is the other, like “Time is a thief,” implying that time takes moments away.
In contrast, hyperbole is an extreme exaggeration used for emphasis, like “I’ve told you a million times!” It doesn’t compare things but stretches the truth for dramatic effect.
While metaphors add depth and symbolism, hyperboles create impact and intensity, often making statements sound more humorous or emotional.
Metaphor and Hyperbole in Literature
Hyperbole vs Metaphor are powerful literary devices that enhance storytelling. Writers use metaphors to create deep, symbolic meanings, like in Shakespeare’s “All the world’s a stage,” comparing life to a performance.
Hyperbole, on the other hand, adds dramatic flair by exaggerating reality, such as in “I’m so hungry I could eat a horse.” Both techniques make language more vivid, helping readers connect emotionally.
From poetry to novels, these figures of speech shape the way we experience literature, adding richness, depth, and expressive power to the text.
Hyperbole: Definition and Usage
Hyperbole is a figure of speech that uses extreme exaggeration to create emphasis or humor. It is not meant to be taken literally but helps express strong emotions or make a point.
For example, saying “I’ve told you a million times!” doesn’t mean exactly a million times, but it stresses repetition. Writers, poets, and advertisers use hyperbole to grab attention and make ideas more memorable.
This technique adds drama and intensity, making language more expressive and engaging in everyday conversations, literature, and media.
hyperbole Usage
Hyperbole is a powerful tool for adding humor, emphasizing key points, and creating dramatic effects. It enhances storytelling by intensifying emotions and actions, making narratives more engaging.
Understanding how to use hyperbole effectively requires considering the context. In conversation, it exaggerates for comedic impact, while in writing, it highlights significance.
Hyperbole in poetry and prose deepens emotional expression, drawing readers in. NLP research examines how context shapes hyperbole usage in communication. When used well, hyperbole makes statements more memorable, amplifying their emotional weight and leaving a lasting impression.
Synonyms of hyperbole
Here are ten words related to “hyperbole”:
- Exaggeration
- Overstatement
- Amplification
- Magnification
- Embellishment
- Overkill
- Extravagance
- Rhetoric
- Elaboration
- Inflation
How to Use Metaphors in Everyday Communication
Using metaphors in everyday communication makes conversations more vivid and engaging. Metaphors create strong mental images, helping people understand complex ideas in a simple way.
Saying “time is money” instantly conveys the value of time without explanation. In speeches, writing, and casual talks, metaphors add depth and emotion, making words more impactful.
They are widely used in marketing, storytelling, and even in daily interactions. When used effectively, metaphors strengthen messages, enhance persuasion, and make communication more memorable and relatable.
Email Example with a Metaphor:
Subject: Project Update
“The project is a marathon, not a sprint. We’re making steady progress, and I’m confident we’ll reach the finish line strong.”
How to Use Hyperbole in Everyday Communication
Using hyperbole in everyday communication adds excitement, humor, and emphasis to conversations. When someone says, “I’m so hungry I could eat a horse,” they don’t mean it literally, but it highlights extreme hunger.
Hyperbole makes speech more expressive, helping to grab attention and create strong impressions. It is commonly used in storytelling, marketing, and casual conversations to add dramatic effect.
Whether exaggerating for humor or making a point stronger, hyperbole enhances communication by making it more engaging, entertaining, and emotionally impactful.
Side by Side Comparison
| Aspect | Metaphor | Hyperbole |
| Definition | A direct comparison between two unrelated things | An exaggerated statement to emphasize a point |
| Purpose | To explain or describe by making an implicit comparison | To create emphasis by exaggerating |
| Literal vs. Figurative | Always figurative | Figurative, often exaggerated to a great extent |
| Use Cases | Clarifying complex ideas, creating impact | Adding humor, exaggeration, or intensity |
Everyday Usage Examples
Hyperbole and metaphor are both powerful tools in language, but they serve different purposes. A hyperbole is an extreme exaggeration, while a metaphor creates a direct comparison between two unrelated things.
For example, saying “I’ve told you a million times!” is hyperbole because it’s an overstatement to emphasize frustration. On the other hand, “Time is a thief” is a metaphor, as it directly compares time to a thief without using “like” or “as.”
In everyday communication, hyperbole adds drama and humor, while metaphors enhance meaning and depth, making language more vivid and engaging.
Why Do We Use Hyperbole and Metaphor?
We use hyperbole or metaphor to make language more expressive, engaging, and impactful. Hyperbole helps emphasize emotions, create humor, or make a point stronger by exaggerating reality. It adds drama and makes statements more memorable.
Metaphors, on the other hand, create deeper meaning by drawing comparisons between unrelated things, helping us understand complex ideas in a simple way.
Both are essential in storytelling, speeches, and everyday conversations. They shape how we communicate, making our words more vivid, creative, and emotionally powerful.
Why Use a Metaphor?
We use metaphors to make language more vivid and meaningful. They help explain complex ideas by comparing them to familiar concepts, making them easier to understand.
Metaphors create strong imagery, making writing and speech more engaging. They also add depth to communication by expressing emotions and abstract thoughts in a relatable way.
In literature, metaphors enhance storytelling by giving deeper layers of meaning. In everyday life, they make conversations more expressive and memorable, helping people connect with ideas on a deeper level.
Why Use Hyperbole?
We use hyperbole to add emphasis, humor, or drama to our speech and writing. It helps highlight a point by exaggerating a situation beyond reality, making it more engaging and memorable.
Hyperbole creates a strong emotional impact, making ideas stand out. In storytelling, it enhances descriptions, adding intensity and excitement.
In everyday conversations, people use hyperbole to express feelings in a more entertaining way. Whether in literature, advertising, or casual speech, hyperbole grabs attention and makes language more lively and impactful.
metaphor Example
- “The world is a stage.”
- “Time is a thief.”
- “His words were a balm for her troubled soul.”
- “Life is a journey.”
- “She has a heart of gold.”
- “He is the black sheep of the family.”
- “The classroom was a zoo.”
- “Ideas are seeds.”
- “Data is the new oil.”
- “That politician is a snake.”
hyperbole Example
- “I’ve told you a million times.”
- “I’m so hungry, I could eat a horse!”
- “This suitcase weighs a ton!”
- “The line at the amusement park was a mile long.”
- “I’m so tired I could sleep for a year.”
- “I’ve got tons of work to do.”
- “It’s raining cats and dogs.”
- “I laughed my head off.”
- “I’m dying of embarrassment.”
- “This is the worst day of my life.”
READ MORE ……“Humans” or “Humen
FAQS:
What is the difference between a hyperbole and a metaphor?
A hyperbole is an extreme exaggeration, while a metaphor is a direct comparison between two unrelated things.
What is the difference between a metaphor and a hyperbolic?
A metaphor compares two things symbolically, whereas something hyperbolic is simply exaggerated for effect.
Is “it’s raining cats and dogs” a metaphor or hyperbole?
“It’s raining cats and dogs” is a metaphor because it compares heavy rain to animals falling from the sky.
Is exaggeration a metaphor or hyperbole?
Exaggeration is a hyperbole because it stretches reality beyond its limits for emphasis.
What is a metaphor example?
“Time is a thief” is a metaphor because it directly compares time to a thief stealing moments from life.
Conclusion
Metaphors vs hyperboles are valuable tools in language. Each serves a unique purpose. Metaphors create understanding through comparison.
Hyperboles amplify meaning through exaggeration. By understanding and using these figures of speech effectively, you can enrich your communication and captivate your audience.
How to use metaphors in writing and speech is an art. This enhances clarity and engagement. Mastering both metaphors and hyperboles will elevate communication. The metaphor and hyperbole difference is fundamental. BERT and GPT for metaphor detection are advancing the field.