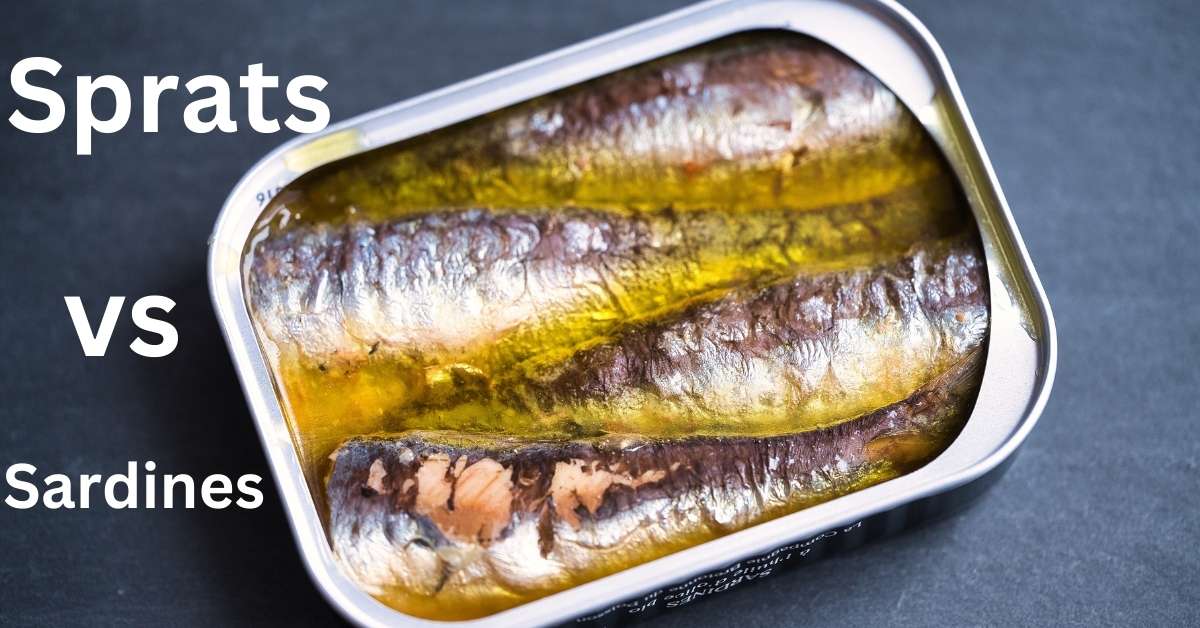
When it comes to small oily fish, sprats vs sardines is a popular debate. Both of these fish are known for their impressive nutritional benefits, particularly their high levels of omega-3 fatty acids, protein content, and vitamin D, all of which contribute to promoting heart health and supporting overall well-being.
However, despite their similarities, sprats vs sardines differ in size, flavor, and culinary uses. Whether you’re looking for a sustainable seafood option, a nutritious snack, or a flavorful ingredient for your next meal, understanding the differences between sprats and sardines can help you make an informed choice. Let’s dive into the details of these two popular fish!
Quick Summary
At first glance, sprats vs sardines might appear quite similar. Both are small oily fish rich in omega-3 fatty acids, and they have nutritional benefits that support heart health and provide a good amount of protein content.
However, the two differ in several important ways, from their size to their flavors and how they are typically consumed. Sardines, often part of the sardine family, tend to be larger and more robust in flavor compared to sprats, which are smaller and milder in taste.
Sardines are commonly found in Mediterranean cuisine and are often available as canned fish or smoked sprats, making them a convenient option. In contrast, sprats, mainly found in Europe, are usually enjoyed smoked or pickled.
Understanding these differences can help you make a more informed decision on which fish is best suited for your next meal.
Understanding Sprats vs Sardines
Both sprats and sardines belong to the herring family, but they belong to different branches. Sardines are typically larger and can grow up to 8 inches, while sprats are smaller, generally about 5 inches in length.
Despite their size difference, both fish are similar in appearance, with silver-colored scales and a similar body shape. Sardines are typically found in warm Mediterranean waters, while sprats are more common in colder European seas, especially the North and Baltic Seas.
The flavor profiles also differ. Sardines have a stronger, more pronounced taste, making them a popular choice for Mediterranean cuisine. Sprats, on the other hand, are milder and have a delicate texture, often enjoyed smoked or used in a variety of European recipes. Both fish offer a host of nutritional benefits, particularly when it comes to omega-3 fatty acids and vitamin D.
Origins of the Sprats
Sprats are native to the colder waters of Northern Europe. Commonly found in the North Sea and the Baltic Sea, European sprats are smaller fish that thrive in large schools. They are often smoked or preserved in salt to extend their shelf life, making them popular in European countries like the UK, Poland, and Sweden.
In these regions, smoked sprats are a beloved snack, served with bread or enjoyed as part of a hearty meal. Sprats are also part of the sardine family, though they are distinct from sardines in their size and texture.
In terms of seafood conservation, sprats are generally fished using sustainable practices. Many sprat fisheries are certified for their environmental sustainability, ensuring that the fish are harvested responsibly and that their populations remain healthy.
Origins of the Sardines
Sardines, on the other hand, have a rich history in the Mediterranean. They were named after the Italian island of Sardinia, where these fish were once abundant. Today, sardines are widely caught in Mediterranean waters and along the coastlines of Europe.
Known for their robust flavor, sardines on toast is a classic dish enjoyed throughout the Mediterranean. Sardines are often sold as canned fish, which makes them an easy and convenient meal option.
Much like sprats, sardines are caught sustainably in many regions, with several fisheries adhering to strict guidelines to protect the fish population and ensure their continued availability. Sardines are also highly regarded for their nutritional benefits, particularly their high levels of omega 3 fatty acids, which are excellent for promoting heart health.
The 5 Key Differences Between Sprats and Sardines
When comparing sprats vs sardines, there are a few key differences that stand out:
- Size: Sardines are larger, typically growing up to 8 inches, while sprats usually reach only about 5 inches.
- Flavor: Sardines have a stronger, more intense flavor, while sprats are milder and more delicate.
- Nutritional Content: Both are high in omega-3 fatty acids, but sardines tend to have a higher concentration of vitamin D and calcium.
- Culinary Uses: Sardines are widely used in Mediterranean cuisine, often grilled or canned. Sprats are often smoked or pickled and are a common snack in Europe.
- Habitat: Sardines thrive in warm Mediterranean waters, while sprats are found in colder European seas like the North and Baltic Seas.
Sprats: Definition and Usage
Sprats are small, oily fish that are primarily found in the European sprats family. Known for their delicate flavor, they are often enjoyed smoked sprats or pickled in various dishes. These fish are typically smaller than sardines, making them a lighter option for a quick snack or addition to meals. Smoked sprats are often served with crackers or used as a topping for salads.
In terms of healthy eating, sprats offer a wealth of nutritional benefits, including omega-3 fatty acids and protein content. These nutrients are essential for heart health and overall wellness, making sprats a great addition to a balanced diet.
Sardines: Definition and Usage
Sardines, often known for their strong and flavorful taste, are part of the sardine family. These fish are larger than sprats and are commonly preserved by canning. Canned fish, especially canned sardines, are a popular and convenient food option worldwide. Sardines are widely used in Mediterranean cuisine and can be found in dishes like sardines on toast, or served in pasta and salads.
With their high levels of omega-3 fatty acids, protein content, and vitamin D, sardines are often touted as one of the best fish options for boosting heart health and improving overall nutrition.
Unlocking the Nutritional Secrets of Sprats

Sprats offer a variety of nutritional benefits. They are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which are known for supporting heart health and reducing inflammation. In addition to their heart-healthy fats, sprats are a great source of protein content, providing the building blocks for muscle repair and growth. These small fish also contain vitamin D, which is crucial for bone health and immune system support.
Since sprats are smaller fish, they tend to accumulate less mercury than larger fish, making them a safer choice for regular consumption. Additionally, sprats are considered a sustainable seafood option, as they are caught in responsible fisheries that focus on protecting marine ecosystems.
Sardines: The Ultimate Nutrient Champions
Sardines are often considered the ultimate nutrient champions due to their high concentration of essential nutrients. Like sprats, they are packed with omega-3 fatty acids, which support heart health and brain function. Sardines are also rich in protein content, which is important for maintaining healthy muscles and tissues. Furthermore, they are an excellent source of vitamin D, which helps regulate calcium levels and supports immune function.
Due to their sustainable seafood practices, sardines are widely considered an eco-friendly choice. Many sardine fisheries follow guidelines for environmental sustainability, ensuring that these fish are responsibly harvested and not overfished.
Comparing Mercury Levels and Environmental Sustainability
Both sprats and sardines are considered low in mercury, which makes them safer to eat compared to larger fish like tuna or shark. These smaller fish do not accumulate high levels of mercury because they are lower on the food chain, which is an advantage for anyone looking to consume healthy eating options without the risk of heavy metal contamination.
In terms of environmental sustainability, both sprats and sardines are generally harvested using responsible fishing methods. Choosing sustainable seafood options, such as canned sardines or smoked sprats, helps protect ocean ecosystems and ensures that fish populations remain healthy for generations to come.
Choosing Between Sprats and Sardines: A Nutritional Guide
When choosing between sprats vs sardines, consider your specific nutritional needs and culinary preferences. If you’re looking for a lighter, milder fish that’s rich in omega-3 fatty acids and protein content, sprats may be the better option. If you prefer a larger, more flavorful fish that’s high in vitamin D and calcium, then sardines are a great choice.
Both fish are excellent sources of essential nutrients and can be enjoyed in a variety of dishes, from simple snacks to more elaborate meals. As part of a healthy eating routine, either fish can offer great nutritional benefits.
Embrace the Health Benefits of Sprats and Sardines
Both sprats and sardines provide significant nutritional benefits, making them a valuable part of any diet. Packed with omega-3 fatty acids, these fish help promote heart health and reduce inflammation.
Additionally, both fish are rich in protein content, which is essential for muscle building and repair. Sardines, in particular, are high in vitamin D, which is important for maintaining healthy bones and supporting the immune system.
Incorporating sprats and sardines into your meals is an easy way to boost your intake of these important nutrients, while also enjoying a tasty and sustainable seafood option.
Side-by-Side Comparison
| Feature | Sprats | Sardines |
| Size | Smaller (up to 5 inches) | Larger (up to 8 inches) |
| Flavor | Milder, delicate flavor | Stronger, richer flavor |
| Omega-3 Fatty Acids | High | Very high |
| Vitamin D | Moderate | High |
| Calcium | Moderate | High |
| Culinary Use | Smoked, pickled, salads | Grilled, canned, sandwiches |
| Sustainability | Sustainable seafood | Sustainable seafood |
READ MORE ….grammershine
Everyday Usage Examples
Both sprats and sardines are versatile and easy to add to everyday meals. You can enjoy sardines on toast for breakfast, toss them into a salad for lunch, or add them to a pasta dish for dinner. Smoked sprats make for a tasty snack, or they can be added to soups and stews.
FAQs:
Are sprats healthier than sardines?
Sprats are equally healthy, offering similar omega 3 fatty acids and protein content, but sardines tend to have more vitamin D and calcium.
Do sprats taste like sardines?
No, sprats have a milder, more delicate flavor compared to the stronger, richer taste of sardines.
Are sprats high in mercury?
No, sprats are low in mercury, as they are small fish lower on the food chain.
What is healthier than sardines?
Fish like salmon or mackerel, which are also rich in omega-3 fatty acids and vitamin D, are just as healthy, if not more.
What is the most unhealthy fish to eat?
Shark, swordfish, and king mackerel are often considered the most unhealthy due to high mercury levels.
Conclusion
sprats vs sardines debate, both fish offer valuable nutritional benefits, including high levels of omega 3 fatty acids, protein content, and vitamin D, making them excellent choices for a healthy diet.
While sardines tend to have a stronger flavor and are often used in Mediterranean cuisine, sprats are milder and commonly enjoyed smoked or pickled in European dishes.
Ultimately, whether you choose sprats or sardines depends on your taste preferences and dietary needs, but both are sustainable seafood options packed with essential nutrients.